
There are several differences between chromatin and chromosome. Difference between chromatin and chromosome These are functional at certain point of development. It is permanently silenced and transcriptionally inactive.įacultative heterochromatin- These regions of euchromatin are converted in heterochromatin. It is found in pericentromeric and telomeric regions of the chromosomes. heterochromatin can be of two types – constitutive and facultative.Ĭonstitutive heterochromatin – remains condensed in G0 stage and contain highly repetitive sequences. Euchromatin is characterized by histone acetylation and methylation. Contrastingly, heterochromatin is the darkly stained region that remains inactive, and transcriptionally silent. This region is transcriptionally active and contains protein-coding regions. These proteins belong to the family of chromosomal ATPase.Įuchromatin regions are lightly stained less condensed part of chromatin that performs the metabolic activities. Condensin proteins are also called structural maintenance of chromosome (SMC). In eukaryotic cell, there are two types of condensins referred as condensin I and condensin II. The chromosome scaffold contains mainly non-histone proteins including condensing, type II topoisomerase, and kinesin. Metaphase chromosomeįurther compaction of 30 nm requires scaffold proteins – the condensin proteins that form chromosome scaffold structure. In zigzag model, two strands comprising stacked nucleosome are folded in left- handed helix which implies interactions between alternate nucleosomes. In solenoid model, adjacent nucleosomes can interact with each other. Finally the solenoid rings are grouped together and form the scaffold. About six nucleosomes together form a single solenoid ring which are linked by 6 H1 linker histones. In this structure, nucleosomes are further packed forming a helix. Solenoid model constitutes the 30 nm structure of chromatin fibre. Two models are formed at this stage – the solenoid and zigzag model. Nonpolar interactions between histone proteins and deoxyribose sugar derivativesĪfter the compaction of DNA around the histones, the second level of chromatin organization is the compaction of 11 nm fiber into 30 nm diameter fibre.Hydrogen bonds present between DNA and the amide groups of amino acids.Hydrogen bonds and salt bridges between the side chains of the positively charged amino acids and negatively charged phosphate groups of DNA backbone.Interactions that occur between histone proteins and DNA Together with linker histones, nucleosomes are called chromatosomes. DNA is wrapped around these histone proteins. The nucleosome core contains dimmers of two H2A, H2B, and tetramer of H3 and H4. H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 form the core histones while H1/H5 is present as the linker histones. Histones are highly basic proteins, rich in lysine and arginine residues, and form the structural support for the chromosome.
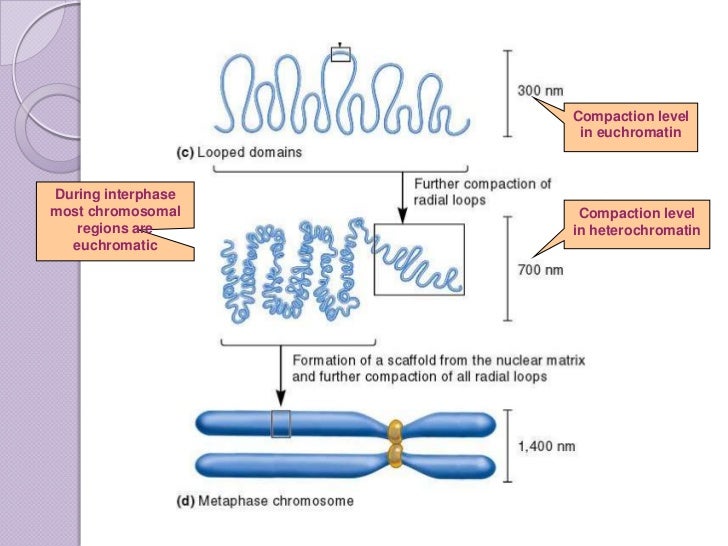
During cell division, interphasic less condensed DNA is compacted into cylindrical, parallel metaphase chromosomes.īasic units of chromatin structure – Nucleosome Under the electron microscope, nucleoprotein complex chromatin appears as beads on a string. Each unit of chromatin is called a nucleosome which contains the protein component histone and DNA. The only difference is chromatin is less condensed, extended DNA while chromosomes are condensed and compact DNA. This article will provide 5 important insights regarding chromosomes and chromatin.Ĭhromatin is the simplest form of DNA organization that undergo various structural modifications and form the compact chromosomes.īasically, chromosomes and chromatin are the same things, both are the type of DNA organization. Chromatin is a nucleoprotein complex that plays important role in the transfer of genetic material that is folded into compact chromosome. They are different levels of DNA arrangements.Īll chromosomes have chromatin.

Chromatin and chromosome are related to each other.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
